ACME
ENTERPRISE This is an EJBCA Enterprise feature.
The Automatic Certificate Management Environment (ACME) is a protocol that a Certificate Authority (CA) and an applicant can use to automate the process of verification of the ownership of a domain (or another identifier) and certificate management.
Supported Operations
EJBCAs ACME implementation currently complies with the final ACME standard IETF - RFC8555. All operations must be called with POST requests. For the directory operation, there is a GET request offered, and for the newNonce operation a GET and HEAD request as well.
|
Operation |
URL |
Description |
RFC 8555 Reference |
|
directory |
/ejbca/acme/directory |
Get the directory object listing all ACME operation URLs and the ACME configuration meta data. |
|
|
newNonce |
/ejbca/acme/newNonce |
Before any POST action is performed, the client needs to retrieve an anti-replay nonce from the server. |
|
|
newAccount |
/ejbca/acme/newAccount |
Create a new ACME account, or retrieve an existing account, including the account URL and the account ID. |
|
|
updateAccount |
/ejbca/acme/acct/{accountId} |
Update or deactivate an existing account. Change its contact information or agree to the new ACME Terms of Service if they have changed. |
|
|
newOrder |
/ejbca/acme/newOrder |
Create a new ACME order for one or multiple domains (or other identifiers). This is the first step to request certificate issuance. |
|
|
challenge |
/ejbca/acme/acct/{accountId}/chall/{challengeId} |
Tell the ACME server that it can validate your challenge response and retrieve the challenge object. |
|
|
newAuthz |
/ejbca/acme/newAuthz |
Only if Pre-Authorization Allowed is enabled in the Alias configuration. |
|
|
finalizeOrder |
/ejbca/acme/acct/{accountId}/orders/{orderId}/finalize |
Send your Certificate Signing Request (CSR) and let the CA issue your certificate. |
|
|
revokeCert |
/ejbca/acme/revokeCert |
Revoke a certificate. |
|
|
keyChange |
/ejbca/acme/keyChange |
Replace the key of an existing account. |
|
|
cert |
/ejbca/acme/cert/{certificateId} |
Download a certificate. |
URL Endpoints and Aliases
The ACME service is available on the following URLs.
Some ACME clients (like PJAC) may cut the URL query string (?configurationId=<alias_name>). Use the URL style with the alias name specified in the URL path.
If the user adds or removes an alias, it is set as the default ACME alias, if the operation results in exactly one alias.
An alias must consist of 1 to 250 alphanumeric non-blank characters case-sensitive including minus '-' and underscore'_'.
|
Default alias with client authentication |
https://<server>:8443/ejbca/acme/directory |
|
Default alias without client authentication |
https://<server>:8442/ejbca/acme/directory |
|
Custom alias <alias_name> with client authentication |
https://<server>:8443/ejbca/acme/directory?configurationId=<alias_name> |
|
Custom alias <alias_name> without client authentication |
https://<server>:8442/ejbca/acme/directory?configurationId=<alias_name> |
EJBCA Specifics
Approvals in EJBCA for updating an end entity or certificate revocation cannot be used with ACME. Only approvals for ACME account management are supported.
All ACME operations are performed over the peers protocol. Thus it is perfectly possible to use an external RA running EJBCA as an ACME proxy.
Validators for CAA checking etc. are configured as described in Validators Overview.
You need to set up separate aliases for each end entity profile/certificate profile and CA.
End entities are managed in RA mode, which means end entities are created or reset (status = NEW) before a certificate is enrolled. This implicates that the 'Finish User' function available in the CA settings does not impact certificate enrollment with ACME (see CA Fields).
ACME Client Specifics
Each ACME client like Certbot or acme.sh might require their unique restriction to enroll certificates. Additionally, you must ensure that the certificate request posted by the ACME client fulfills the CA and profile restrictions. That is, enroll a certificate for several identifiers, additional subject DN attributes, certificate validity, or restrictions on the key specification used.
Subject-DN attributes and subject-AN DNS entries are configured in the end entity profiles. For more information, see End Entity Profiles Fields and End Entity Profile Configuration.
Key specification and certificate validity (usually < 1 year, or 6 months with Certbot 1.18) are configured in the certificate profiles, see Certificate Profile Fields.
Configuration
End Entity Profile Configuration
Besides requirements depending on your ACME client or individual requirements of your certificate request, the following settings should be used for an end entity profile used with ACME.
A certificate enrolled with ACME for one identifier only, must have at least one additional DNS SAN field.
|
Field |
Value |
|
Username |
Leave empty |
|
Password (or Enrollment Code) |
Leave empty |
|
Batch generation (clear text pwd storage) |
Enable if you reset the end entity for certificate enrollment. If you do not generate RANDOM with the RA name generate scheme, you must enable this option. |
|
End Entity E-mail |
Use, Not Required, Modifiable |
|
Subject DN Attributes |
|
|
CN, Common name |
Required, Modifiable |
|
Default Certificate Profile |
<The certificate profile to use> |
|
Default CA |
<The CA signing the certificate> |
|
Default Token |
User Generated |
|
Other subject attributes |
|
|
SAN DNS Name or IP address |
Not required, Modifiable. Add as many DNS or IP identifiers as you require for your certificates. |
Certificate Profile Configuration
Beside your ACME client used or individual requirements of your certificate request, the following settings should be used for a certificate profile used with ACME.
|
Field |
Value |
|
Available Key Algorithms |
Choose allowed key algorithms |
|
Available ECDSA curves |
Choose allowed ECDSA key algorithms |
|
Available Bit Lengths |
Choose desired key length in case of RSA keys |
|
Validity or end date of the certificate |
Validity. I.e. 6mo, 1y or 395d. |
|
Extended Key Usage |
Server Authentication |
|
Approvals |
Clear. Ensure to not select any Approvals as EJBCA supports approvals for ACME account management only. |
|
Available CAs |
<The CA signing the certificate> |
|
Single Active Certificate Constraint |
Revokes all previously enrolled certificates of an end entity enrolled with this or another certificate profile with this option enabled. Only relevant if the end entity name is not generated randomly using the RA name generation scheme. |
Enabling ACME
The ACME protocol is by default disabled. To enable the service, go to CA UI > System Configuration > Protocol Configuration and select Enable for ACME.
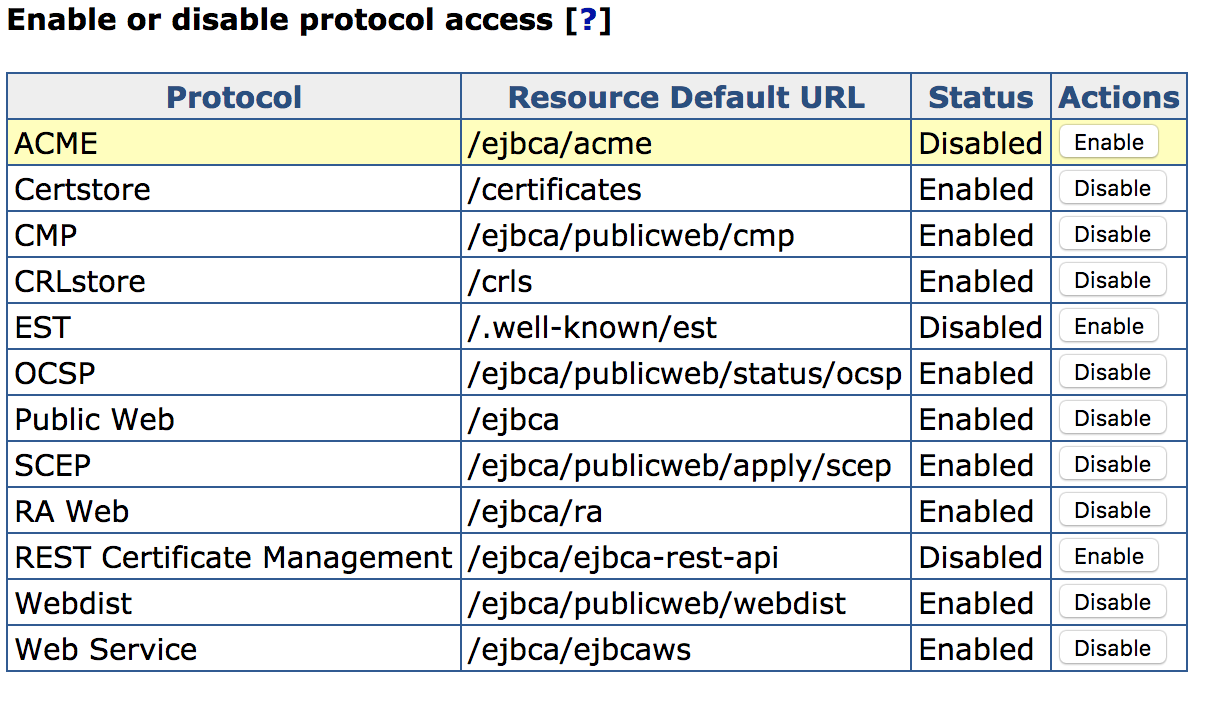
Managing ACME Alias Configurations
Much like other protocols in EJBCA, several different ACME configurations can be maintained at the same time using aliases.
To configure ACME, select ACME Configuration
under the
System Configuration menu.
Before an ACME alias can be used it must be edited and stored, even if its configuration remains unchanged.
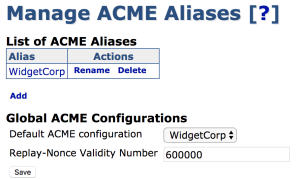
Global Fields
The following fields are defined globally for all ACME operations.
|
Field |
Description |
|
Default ACME Configuration |
The configuration to use if the specified alias does not exist. |
|
Replay Nonce Validity Number |
Defines the validity in milliseconds of a generated replay nonce. |
ACME Alias Configuration
Initial ACME Alias configuration.
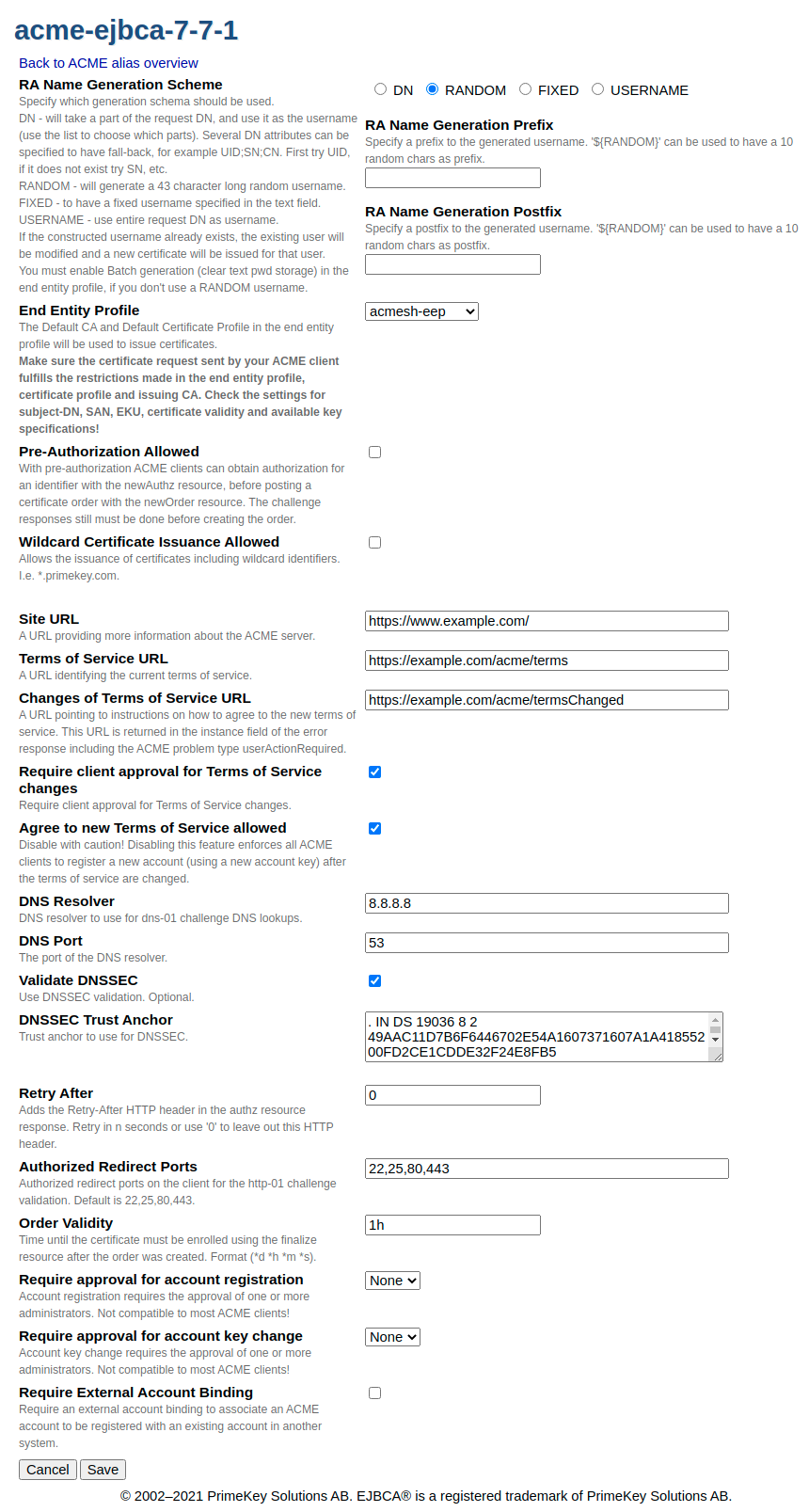
Initial ACME Alias configuration.
The following table lists ACME specific fields for each individual alias in more detail.
|
Field |
Description |
|
RA Name Generation Scheme |
DN: Will take a part of the request DN, and use it as the username (use the list to choose which parts). Several DN attributes can be specified to have a fall-back. For example: UID;SN;CN. First, try UID. If it does not exist try SN, etc.
Enable Batch generation in the end entity profile, if you don't use RANDOM usernames (see End Entity Profile Configuration). |
|
RA Name Generation Prefix |
Specify a prefix to the generated username. '${RANDOM}' can be used to have 12 random chars as prefix. |
|
RA Name Generation Postfix |
Specify a postfix to the generated username. '${RANDOM}' can be used to have 12 random chars as postfix. |
|
End Entity Profile |
The end entity profile to use for end entities enrolled using this alias. The CA signing the certificate is the default CA of this end entity profile, and the certificate profile used for the certificate is the default certificate profile of this end entity profile.
|
|
Pre-Authorization Allowed |
Pre-authorization, as defined in section 7.4.1 of RFC 8555. |
|
Wildcard Certificate Issuance Allowed |
Whether this alias can be used to issue certificates with wildcard DNS names in their SANs. Refer to section 7.1.3 of RFC 8555. |
|
Wildcard Certificate with http-01 Challenge Allowed |
If disabled, no http-01 challenge for identifiers with a wildcard (i.e. *.primekey.com) is generated. Only active if 'Wildcard Certificate Issuance Allowed' is enabled. Default: enabled. |
|
Site URL |
URL to a website describing this CA. Optional. Refer to section 7.1.1 of RFC 8555. |
|
Terms of Service URL |
URL to your terms of service for ACME. Refer to section 7.1.1 of RFC 8555. |
|
Changes of Terms of Service URL |
URL to advise how to handle changes of your terms of service for ACME. Refer to section 7.3.1 of RFC 8555. |
|
Require client approval for Terms of Service changes |
Specifies whether users must approve the new version if the Terms of Service URL is changed. Default: enabled. |
|
Agree to new Terms of Service allowed |
Specifies whether users are allowed to agree to new Terms of Service after they have changed. ACME clients must request the updateAccount resource with termsOfServiceAgreed set to true. If not allowed, clients have to request a new account (including new keys). Only active if Require client approval for changes of Terms of Service is enabled. Default: enabled. |
|
DNS Resolver |
A specified DNS resolver, used when processing dns01 challenges. |
|
DNS Port |
Port used for DNS communications. |
|
DNSSEC Trust Anchor |
The ICANN trust anchor, configurable should it ever change. |
|
Retry After |
Value used to indicate that client should try polling the authorization endpoint again after a while (in seconds). Default is 0 and this is used mainly for clients such as cert-manager which send post-as-get request while waiting for ACME server to prepare the challenge. |
|
Authorized Redirect Ports |
List of authorized ports for client side redirects for the http-01 challenge validation for DNS identifiers. Default is 22,25,80,443. Leave empty for no restrictions. |
|
Order Validity |
The time span within the challenges for the orders identifiers have to be completed. Format is human readable validity with second precision, i.e. 10d 12h or 30s 30m 1h. The format string is normalized when the form data is stored. Default value is 1h. |
|
Require approval for account registration |
Approval profile to be applied for ACME account registration, see Approvals. Default: None. |
|
Require approval for account key change |
Approval profile to be applied for ACME account key change, see Approvals. Default: None. |
|
Require External Account Binding |
External Account Binding (EAB), as defined in section 7.4.3 of RFC 8555. |
Managing ACME External Account Bindings (EAB)
If Require External Account Binding is disabled, EAB requests nested in the ACME newAccount request are not considered. Otherwise, an ACME newAccount request without a nested EAB request will fail with an HTTP status code 400 (Bad Request) and the ACME error externalAccountRequired, if the client does not send a valid EAB with the newAccount request.
EJBCA supports the ACME compliant EAB with symmetric key MAC protected EAB requests. Additionally, EJBCA supports EAB with asymmetric private key signature protected EAB requests.
Combine ACME EAB with General Account Binding
The ACME EAB with symmetric key supports the combination with general external account bindings, see External Account Bindings.
The base64Url encoded Key Identifier of the ACME EAB must match one of the external account binding IDs, available in the EAB namespace configured in the relevant certificate profile. It does not matter if the ACME account was registered with this key identifier or if the value was stored after the registration.
ACME EAB with Symmetric Key Configuration
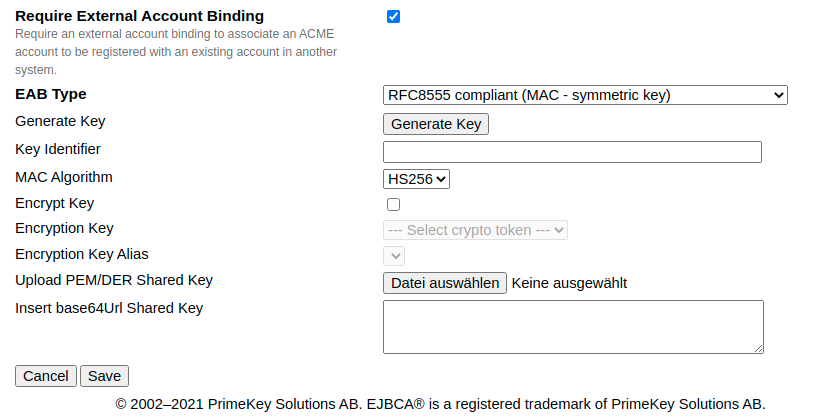
Initial ACME EAB with symmetric key configuration.
RFC8555 compliant ACME EAB
|
Field |
Description |
|
EAB Type |
RFC8555 compliant (MAC - symmetric key) |
|
Generate Key |
Generates a 256 bits AES symmetric key. The key is stored either encrypted or not (see Encrypt Key). It is rendered as base64Url encoded value in the text field Insert base64Url Key. The SHA-1 hash of the AES key is generated and stored as a base64Url encoded value as key identifier and rendered in the text field Key Identifier as is. |
|
Key Identifier |
The secret key identifier of the symmetric key. The value must not be empty, but max. 256 characters long and base64Url encoded. The value does not need to be a fingerprint depending on any known algorithm. It is entered by the user. Since the EAB is stored at the ACME alias configuration, EJBCA only verifies, that the EAB message contains the correct key identifier. |
|
MAC Algorithm |
The secret MAC algorithm to sign the MAC protected EAB request (only HS256 at the time). |
|
Encrypt Key |
Encrypts the shared key in the data store if selected (rendered in clear text in the GUI). |
|
Encryption Key |
The crypto token used to encrypt / decrypt the shared key. |
|
Encryption Key Alias |
The key alias of the crypto tokens key pair used to encrypt / decrypt the shared key. |
|
Upload PEM/DER Key |
Upload PEM or DER encoded symmetric AES key or a byte sequence. If a key is uploaded, the Insert base64Url Key below does not need to be specified and is populated after the form is saved. |
|
Insert base64Url Key |
Symmetric key. The value must not be empty (except a file is uploaded), but max. 512 characters long and base64Url encoded. |
Key Identifier, MAC Algorithm and Insert base64Url Key must be shared with the ACME account holders in order to request a newAccount resource with a valid EAB request. For information on the message format, see newAccount request with RFC8555 compliant EAB.
ACME EAB with asymmetric private/public key configuration.
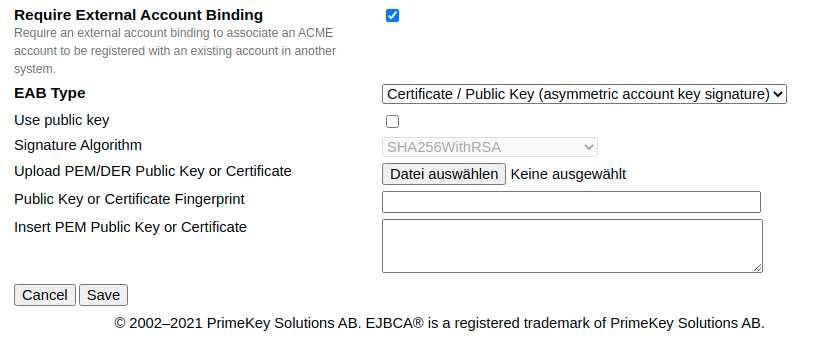
Initial ACME EAB with symmetric key configuration.
Asymmetric key signature protected EAB
|
Field |
Description |
|
EAB Type |
Certificate / Public Key (asymmetric account key signature) |
|
Use public key |
Set to true, if you want to upload a public key or set to false if you want to upload an X.509 certificate. If set to true and a certificate is uploaded, only the public key is stored and the fingerprint is generated using the signature algorithm selected. |
|
Signature Algorithm |
The secret signature algorithm to sign the signature protected EAB request. It is considered only if a public key is used. Otherwise, this field will be filled with the certificate's signature algorithm after the form is saved. |
|
Upload PEM/DER Public Key or Certificate |
Upload PEM or DER encoded RSA or ECDSA public key or X.509 certificate. If a certificate or key is uploaded, the text fields Public Key or Certificate Fingerprint and Insert PEM Public Key or Certificate below do not need to be filled manually but are populated after the form is saved. |
|
Public Key or Certificate Fingerprint |
The public key or certificate fingerprint. The value must not be empty, but max. 256 characters long and base64Url encoded. The value does not need to be a fingerprint depending on any known algorithm. It can be overwritten by the user. Since the EAB is stored at the ACME alias configuration, EJBCA only verifies, that the EAB message contains the correct string. This string might be used as a secret message, which is transmitted on a separate channel. |
|
Insert PEM Public Key or Certificate |
PEM formatted X.509 certificate or RSA or ECDSA public key including boundaries. The value must not be empty, but max. 4096 characters long. |
Public Key or Certificate Fingerprint, Signature Algorithm (in case of public key) and Insert PEM Pulbic Key or Certificate must be shared with the ACME account holders in order to request a newAccount resource with a valid EAB request. The EAB request must be signed either with the certificate's signature algorithm or in the case of a public key, the one given by the user. For more information on the message format, see newAccount request with EAB with asymmetric key signature.
Identifiers and Challenge Validation
EJBCA currently supports the validation of domain and IP identifiers.
Domain identifiers can be validated either using the http-01 or dns-01 challenge as defined in section 8 of RFC 8555. IPv4 or IPv6 identifiers can be validated with http-01 challenge only as defined in section 5 of RFC 8738 (JDK8). IPv6 identifier challenge validation requires a running application server with IPv6 enabled (-Djava.net.preferIPv6Addresses=true, Wildfly14 can be operated with IPv4 or IPv6 only).
HTTP Challenge (http01)
If the client chooses to use the http-01 challenge type, it intends to prove that it controls the domain or IP requested in the certificate by provisioning a resource under the same domain name or IP and port 80, i.e. http://example.org/.well-known/acme-challenge.
DNS Challenge (dns01)
If the client chooses to use the dns-01 challenge type, it instead obligates itself to supply a TXT record containing the same token response as described above. As per RFC 8555, DNSSEC is required for dns01 challenges.
Approvals
Approvals can be used with ACME account management.
Approvals for the newAccount Resource
If approvals are used for the newAccount resource, requests to this resource return an HTTP 500 (Internal Server Error) response including an ACME problem message of type urn:ietf:params:acme:error:serverInternal indicating the state of the created approval request and its request ID. For example, A request to register your ACME account has been sent for approval. RequestID=123456789 after the first ACME resource request has been posted. Further requests return responses in the same matter indicating the state of the approval request either with state PENDING, REJECT, or EXPIRED. If the approval has been accepted, a request to the newAccount resource creates the account and returns the HTTP 201 (Created) as expected. If an approval has expired, it is no longer possible to register the keys for this account and you must generate new keys.
Approvals for the keyChange Resource
If approvals are used for the keyChange resource, requests to this resource return an HTTP 500 (Internal Server Error) response including an ACME problem message of type urn:ietf:params:acme:error:serverInternal indicating the state of the created approval request and its request ID, see example in Approvals for the newAccount Resource. If an approval request has expired, it is renewed automatically if the keyChange resource is requested.
Terms of Service
When an ACME account is initially registered using the newAccount resource, the account holder must agree to ACME service Terms of Service. If 'Require client approval for changes of Terms of Service' is enabled and the Terms of Service have changed, requesting ACME resources except the newAccount resource will fail. To agree to the new ACME service Terms of Service, clients must either register a new account using the newAccount resource (with new keys) or agree to the new Terms of Service using the updateAccount resource (see Workflow examples). Therefore Agree to new Terms of Service allowed must be enabled.
Compatibility with ACME Clients
EJBCA is compatible with the following ACME clients (listed in Letsencrypt's list of compatible ACME clients). For information on installation and use, see the respective ACME client section:
Swagger UI
Swagger UI allows you to visualize and interact with the API’s resources. The Swagger UI playground is available in your browser on the URL https://localhost:8443/ejbca/swagger-ui (use port 8443 since ACME uses client certificate authentication).
You can switch between displaying ACME or the REST API using the Swagger UI Select a spec list.
The Swagger UI is only available if you build EJBCA in non-production mode, i.e. with ejbca.productionmode=false set in conf/ejbca.properties.
The Swagger UI for ACME will only be available if ACME is activated as a protocol, see Enabling ACME.
Request Examples
The following lists ACME operations to perform in order to get a certificate. For newAccount and for revokeCert requests there MUST be a 'jwk' field, otherwise a 'kid' field.
getDirectory request
Returns the URLs for each ACME operation and the service metadata.
GET /acme/directory HTTP/1.1{ "newNonce":"https://footrust.local:8443/ejbca/acme/newNonce", "newAccount":"https://footrust.local:8443/ejbca/acme/newAccount", "newOrder":"https://footrust.local:8443/ejbca/acme/newOrder", "newAuthz":"https://footrust.local:8443/ejbca/acme/newAuthz", "revokeCert":"https://footrust.local:8443/ejbca/acme/revokeCert", "keyChange":"https://footrust.local:8443/ejbca/acme/keyChange", "meta":{ "termsOfService":"https://footrust.com/acme/terms", "website":"https://footrust.com", "caaIdentities":[ "footrust.com" ], "externalAccountRequired":false }}newAccount request
Creates a new ACME account to EJBCA and returns it with the response. EJBCA uses a public key to verify the JWS (that is, the jwk element of the JWS header) to authenticate future requests from the account. EJBCA supports RSA and EC key types. If the account with this key already exists, it is returned with the response.
POST https://localhost:8442/ejbca/acme/newAccount HTTP/1.1Content-Type: application/jose+json{ "protected": base64url({ "alg": "ES256", "jwk": {...}, "nonce": "6S8IqOGY7eL2lsGoTZYifg", "url": "https://example.com/acme/newAccount" }), "payload": base64url({ "contact": [ "mailto:cert-admin@example.com", "tel:+12025551212" ], "termsOfServiceAgreed": true }), "signature": "RZPOnYoPs1PhjszF...-nh6X1qtOFPB519I"}newAccount request with RFC8555 compliant EAB
Creates a new ACME account to EJBCA and returns it with the response.
The nested EAB request is signed using a symmetric key and HMAC algorithm shared by the CA.
POST https://localhost:8442/ejbca/acme/newAccount HTTP/1.1Content-Type: application/jose+json{ "protected": base64url({ "alg": "ES256", "jwk": {...}, "nonce": "6S8IqOGY7eL2lsGoTZYifg", "url": "https://example.com/acme/newAccount" }), "payload": base64url({ "contact": [ "mailto:cert-admin@example.com", "tel:+12025551212" ], "termsOfServiceAgreed": true, "externalAccountBinding": { "protected": base64url({ "alg": "HS256", "kid": /* key identifier from CA */, "url": "https://example.com/acme/newAccount" }), "payload": base64url(/* same as in "jwk" above */), "signature": /* MAC using MAC key from CA */ } }), "signature": "RZPOnYoPs1PhjszF...-nh6X1qtOFPB519I"}newAccount request with EAB with asymmetric key signature
Creates a new ACME account to EJBCA and returns it with the response.
The nested EAB request is signed by the same JWK that signed the outer message. Compared to the standard EAB request (see above), this EAB requests payload contains a map including the account key to be registered. Additionally, this map contains the public key or certificate fingerprint shared by the CA and the signature over the account key by a private key shared with the CA and the agreed signature algorithm.
POST https://localhost:8442/ejbca/acme/newAccount HTTP/1.1Content-Type: application/jose+json{ "protected": base64url({ "alg": "ES256", "jwk": {...}, "nonce": "6S8IqOGY7eL2lsGoTZYifg", "url": "https://example.com/acme/newAccount" }), "payload": base64url({ "contact": [ "mailto:cert-admin@example.com", "tel:+12025551212" ], "termsOfServiceAgreed": true, "externalAccountBinding": { "protected": base64url({ "alg": "HS256", "url": "https://example.com/acme/newAccount" }), "payload": base64url({ "key": / * same as in "jwk" above * /, "cf": / * certificate or public key fingerprint shared by the CA * /, "aks": / * signature of the account key using the signature algorithm and private key shared by the ACME CA * /, }), "signature": / * MAC using same MAC key that signed the outer JWS message. * / }), "signature": "RZPOnYoPs1PhjszF...-nh6X1qtOFPB519I"}updateAccount request
Updates an ACME accounts contact information.
POST https://localhost:8442/ejbca/acme/acct/evOfKhNU60wg HTTP/1.1Content-Type: application/jose+json{ "protected": base64url({ "alg": "ES256", "kid": "https://example.com/acme/acct/evOfKhNU60wg", "nonce": "6S8IqOGY7eL2lsGoTZYifg", "url": "https://example.com/acme/acct/evOfKhNU60wg" }), "payload": base64url({ "contact": [ "mailto:cert-admin@example.com", "tel:+12025551212" ] }), "signature": "RZPOnYoPs1PhjszF...-nh6X1qtOFPB519I"}updateAccount request and agree to new Terms of Service
Updates an ACME agreement to the new Terms of Service if they have changed. This is a non-RFC compliant function. To use this newAccount request Require client approval for changes of Terms of Service and Agree to new Terms of Service allowed must be enabled.
POST https://localhost:8442/ejbca/acme/acct/evOfKhNU60wg HTTP/1.1Content-Type: application/jose+json{ "protected": base64url({ "alg": "ES256", "kid": "https://example.com/acme/acct/evOfKhNU60wg", "nonce": "6S8IqOGY7eL2lsGoTZYifg", "url": "https://example.com/acme/acct/evOfKhNU60wg" }), "termsOfServiceAgreed": true }), "signature": "RZPOnYoPs1PhjszF...-nh6X1qtOFPB519I"}updateAccount request and account deactivation
Deactivates an ACME account (not reversible).
POST https://localhost:8442/ejbca/acme/acct/evOfKhNU60wg HTTP/1.1Content-Type: application/jose+json{ "protected": base64url({ "alg": "ES256", "kid": "https://example.com/acme/acct/evOfKhNU60wg", "nonce": "ntuJWWSic4WVNSqeUmshgg", "url": "https://example.com/acme/acct/evOfKhNU60wg" }), "payload": base64url({ "status": "deactivated" }), "signature": "RZPOnYoPs1PhjszF...-nh6X1qtOFPB519I"}newOrder request
Creates a new ACME order.
POST /acme/newOrder HTTP/1.1Content-Type: application/jose+json{ "protected": base64url({ "alg": "ES256", "kid": "https://example.com/acme/acct/evOfKhNU60wg", "nonce": "5XJ1L3lEkMG7tR6pA00clA", "url": "https://example.com/acme/new-order" }), "payload": base64url({ "identifiers": [ { "type": "dns", "value": "www.example.org" }, { "type": "dns", "value": "example.org" } ], "notBefore": "2016-01-01T00:00:00Z", "notAfter": "2016-01-08T00:00:00Z" }), "signature": "H6ZXtGjTZyUnPeKn...wEA4TklBdh3e454g"}The newOrder response contains information about challenges. For more information, refer to section 7.5.1 of RFC 8555.
newAuthz request
Request a pre-authorization.
POST /acme/newAuthz HTTP/1.1Host: example.comContent-Type: application/jose+json{ "protected": base64url({ "alg": "ES256", "kid": "https://example.com/acme/acct/evOfKhNU60wg", "nonce": "uQpSjlRb4vQVCjVYAyyUWg", "url": "https://example.com/acme/newAuthz" }), "payload": base64url({ "identifier": { "type": "dns", "value": "example.org" } }), "signature": "nuSDISbWG8mMgE7H...QyVUL68yzf3Zawps"}challenge request
Call EJBCA's ACME service to verify the challenge response, that proves you possess control over the domain.
POST /acme/acct/{accountId}/chall/{challengeId} HTTP/1.1Content-Type: application/jose+json{ "protected": base64url({ "alg": "ES256", "kid": "https://example.com/acme/acct/evOfKhNU60wg", "nonce": "Q_s3MWoqT05TrdkM2MTDcw", "url": "https://example.com/acme/chall/prV_B7yEyA4" }), "payload": base64url({}), "signature": "9cbg5JO1Gf5YLjjz...SpkUfcdPai9uVYYQ"}finalizeOrder request
To generate the certificate.
POST /acme/acct/{accountId}/orders/{orderId}/finalize HTTP 1.1Content-Type: application/jose+json{ "protected": base64url({ "alg": "ES256", "kid": "https://example.com/acme/acct/evOfKhNU60wg", "nonce": "MSF2j2nawWHPxxkE3ZJtKQ", "url": "https://example.com/acme/order/TOlocE8rfgo/finalize" }), "payload": base64url({ "csr": "MIIBPTCBxAIBADBFMQ...FS6aKdZeGsysoCo4H9P", }), "signature": "uOrUfIIk5RyQ...nw62Ay1cl6AB"}The response to the finalizeOrder call is the certificate.
HTTP Status Codes
|
HTTP Status Code |
Description |
|
200 |
Success |
|
201 |
Created |
|
204 |
No content |
|
400 |
Bad request |
|
401 |
Unauthorized |
|
403 |
Forbidden |
|
404 |
Not found |
|
409 |
Conflict |
|
500 |
Internal Server Error |